Scaling
In this example, the time evolution of type scaling is demonstrated. In the scenario, the emissions increase linearly from the year 2019 to the year 2039. The emissions in 2039 are set to be twice as much as in 2019.
Imports
If the openairclim package cannot be imported, make sure that you have installed the package with pip or added the oac source folder to PYTHONPATH.
import xarray as xr
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import openairclim as oac
xr.set_options(display_expand_attrs=False)
<xarray.core.options.set_options at 0x7f7944cc17f0>
Input files
In order to be able to execute this example simulation, three types of input are required.
Configuration file scaling.toml
Emission inventories
ELK_aviation_2019_res5deg_flat.nc
ELK_aviation_2039_res5deg_flat.nc
Time evolution file for scaling: time_scaling_linear_2019-2039.nc
Emission inventories
Source: DLR Project EmissionsLandKarte (ELK)
Resolution down-sampled to 5 deg resolution
Converted into format suitable for OpenAirClim
Inventory years
2019 (original)
2039 (same inventory as original, only year changed)
Time evolution
Time evolution with scaling of emissions
Time period: 2000 - 2050
Linear ramp-up between years 2019 and 2039
evo = xr.load_dataset("source/demos/input/time_scaling_linear_2019-2039.nc")
display(evo)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
evo.scaling.plot(ax=ax)
ax.grid(True)
<xarray.Dataset> Size: 408B
Dimensions: (time: 51)
Coordinates:
* time (time) int32 204B 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 ... 2047 2048 2049 2050
Data variables:
scaling (time) float32 204B 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 ... 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0
Attributes: (5)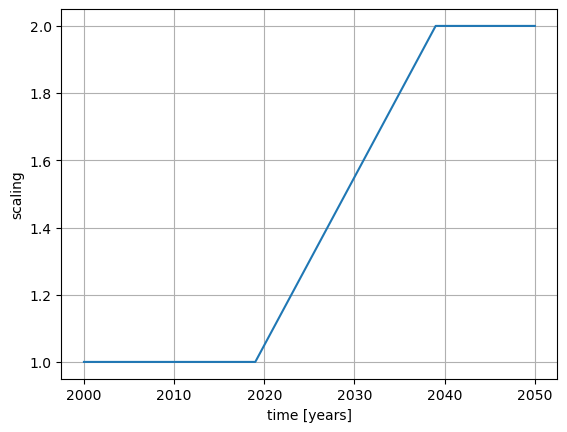
Simulation run
oac.run("source/demos/02_scaling/scaling.toml")
Results
Time series
Emission sums
Concentrations
Radiative forcings
Temperature changes
results_ds = xr.load_dataset("source/demos/02_scaling/results/scaling.nc")
display(results_ds)
<xarray.Dataset> Size: 4kB
Dimensions: (ac: 2, time: 21)
Coordinates:
* ac (ac) <U7 56B 'DEFAULT' 'TOTAL'
* time (time) int64 168B 2019 2020 2021 2022 ... 2036 2037 2038 2039
Data variables:
emis_CO2 (ac, time) float64 336B 849.1 891.6 ... 1.656e+03 1.698e+03
emis_distance (ac, time) float64 336B 5.891e+10 6.185e+10 ... 1.178e+11
emis_H2O (ac, time) float64 336B 332.5 349.1 365.8 ... 648.4 665.0
conc_CO2 (ac, time) float64 336B 0.109 0.2175 0.3272 ... 2.634 2.797
RF_CO2 (ac, time) float64 336B 0.001705 0.003391 ... 0.03858 0.04083
RF_cont (ac, time) float64 336B 0.0664 0.06811 ... 0.09881 0.1005
RF_H2O (ac, time) float64 336B 0.004648 0.00488 ... 0.009296
dT_CO2 (ac, time) float64 336B 0.0001299 0.0003738 ... 0.01773
dT_cont (ac, time) float64 336B 0.002984 0.005714 ... 0.03282 0.03376
dT_H2O (ac, time) float64 336B 0.0004036 0.0007826 ... 0.0057
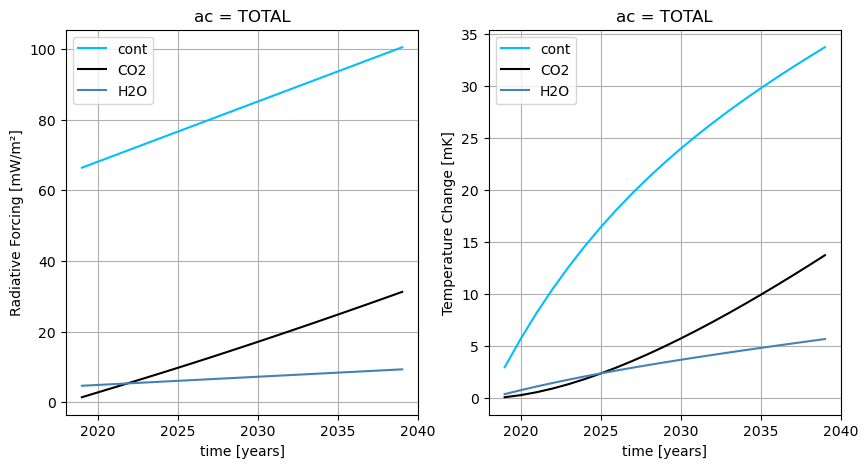
Attributes: (4)# Plot Radiative Forcing and Temperature Changes
ac = "TOTAL"
rf_cont = results_ds.RF_cont.sel(ac=ac) * 1000
rf_co2 = results_ds.RF_CO2.sel(ac=ac) * 1000
rf_h2o = results_ds.RF_H2O.sel(ac=ac) * 1000
dt_cont = results_ds.dT_cont.sel(ac=ac) * 1000
dt_co2 = results_ds.dT_CO2.sel(ac=ac) * 1000
dt_h2o = results_ds.dT_H2O.sel(ac=ac) * 1000
fig, ax = plt.subplots(ncols=2, figsize=(10,5))
ax[0].grid(True)
ax[1].grid(True)
rf_cont.plot(ax=ax[0], color="deepskyblue", label="cont")
rf_co2.plot(ax=ax[0], color="k", label="CO2")
rf_h2o.plot(ax=ax[0], color="steelblue", label="H2O")
dt_cont.plot(ax=ax[1], color="deepskyblue", label="cont")
dt_co2.plot(ax=ax[1], color="k", label="CO2")
dt_h2o.plot(ax=ax[1], color="steelblue", label="H2O")
ax[0].set_ylabel("Radiative Forcing [mW/m²]")
ax[1].set_ylabel("Temperature Change [mK]")
ax[0].legend()
ax[1].legend()
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f7943e0c050>